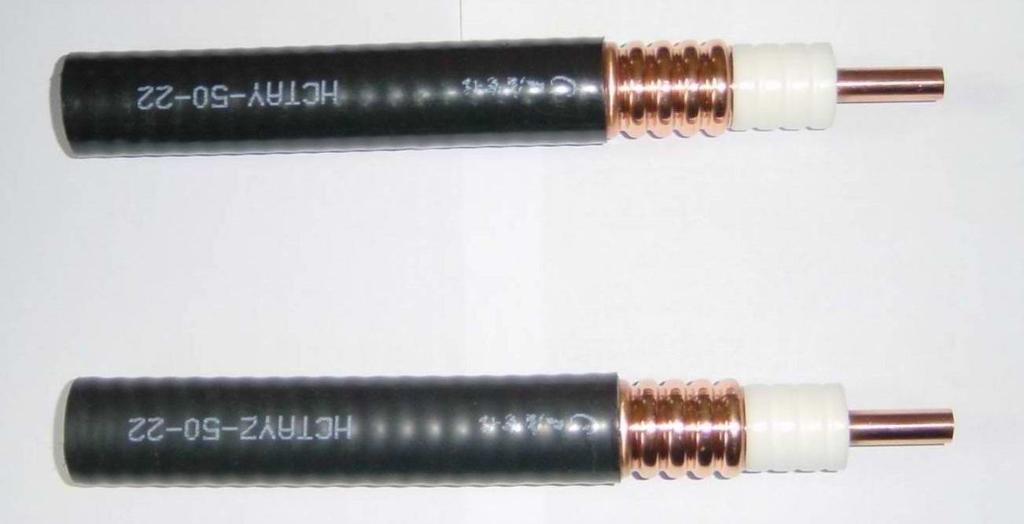
Feeder cables play an essential role in various high-frequency communication systems, offering a reliable pathway for signal transmission between equipment and antennas. These cables are critical in telecommunications, broadcasting, and other industries where seamless data transfer is necessary. One specific type, the RF feeder cable, is commonly used for connecting radio frequency (RF) components. In this article, we will explore the structure, applications, and key considerations when selecting the right feeder cable for your needs.
What is a Feeder Cable?
A feeder cable is a type of coaxial cable used to connect transmitting and receiving equipment to antennas in communication systems. It is designed to maintain signal integrity over long distances, ensuring that transmitted signals remain strong with minimal loss. These cables are primarily used in RF systems, including radio, television broadcasting, and cellular communication networks.
Unlike standard coaxial cables, feeder cables are optimized for transmitting high-frequency signals, making them suitable for long-distance applications. RF feeder cables are a popular variant, specifically designed for RF systems where the frequency of the signal is crucial.
Structure of a Feeder Cable
The structure of a feeder cable is similar to other coaxial cables but with enhanced materials and engineering for improved performance in high-frequency applications. Here’s a breakdown of the components that make up a typical feeder cable:
- Inner Conductor: The inner conductor carries the signal and is made of copper or copper-clad aluminum, providing high conductivity to minimize signal loss. Copper is the preferred material for applications where minimal signal attenuation is required.
- Dielectric Insulation: The dielectric layer surrounds the inner conductor and separates it from the outer conductor. This insulation is typically made of foam or solid polyethylene, depending on the required performance. The dielectric material is designed to reduce signal loss and maintain the integrity of the transmitted signal.
- Outer Conductor (Shield): The outer conductor is usually made of aluminum foil and copper braid, providing effective shielding against electromagnetic interference (EMI). This shielding ensures that external signals do not interfere with the transmitted data, maintaining a clear and strong connection.
- Outer Jacket: The outer jacket is made of PVC, polyethylene, or another durable material that protects the cable from environmental factors such as UV radiation, moisture, and mechanical wear. Feeder cables are often installed in harsh outdoor environments, so the outer jacket must be resistant to environmental degradation.
Types of RF Feeder Cables
RF feeder cables come in various sizes and specifications, each designed to suit specific applications. Here are the most common types of RF feeder cables:
- 50 Ohm Feeder Cable: This is the most commonly used type of RF feeder cable in telecommunications and broadcasting. It offers low signal loss and is ideal for transmitting RF signals in cellular networks, Wi-Fi systems, and other wireless communication systems.
- 75 Ohm Feeder Cable: This type of RF feeder cable is used in applications where lower power is transmitted, such as cable television (CATV) and satellite systems. Although it has a higher attenuation rate than the 50 Ohm version, it is more suitable for shorter distances.
- Low Loss Feeder Cable: These cables are designed with enhanced materials and construction to reduce signal loss over long distances. Low-loss feeder cables are often used in high-frequency applications where maintaining signal strength is critical.
Applications of Feeder Cables
Feeder cables are used in a variety of industries and applications where reliable signal transmission is essential. Here are some of the key areas where RF feeder cables play a vital role:
- Telecommunications: RF feeder cables are widely used in telecommunications systems to connect base stations to antennas. These cables ensure that the RF signal remains strong, reducing the need for additional signal amplifiers and boosters. Cellular networks, Wi-Fi hotspots, and other wireless communication systems rely on feeder cables for efficient data transmission.
- Broadcasting: In radio and television broadcasting, feeder cables are used to connect transmitters to antennas. These cables allow broadcasters to transmit high-frequency signals over long distances with minimal degradation. The quality of the feeder cable directly affects the strength and clarity of the transmitted audio and video signals.
- Military and Aerospace: The military and aerospace industries require reliable communication systems for operations in remote or harsh environments. RF feeder cables are used in radar systems, satellite communication systems, and other RF-based equipment, ensuring that signals are transmitted with minimal interference.
- Wireless Communication: Wireless communication networks, including Wi-Fi, use RF feeder cables to connect antennas to routers and other network devices. The low signal loss of these cables ensures strong and reliable wireless connections.
- Surveillance Systems: In surveillance systems, feeder cable are used to connect cameras and other monitoring equipment to central control units. The integrity of the transmitted video and audio signals is critical for effective surveillance, making high-quality feeder cables an essential component.
Benefits of Using RF Feeder Cables
RF feeder cables offer several benefits that make them ideal for high-frequency communication systems. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Low Signal Loss: The primary benefit of RF feeder cables is their ability to transmit signals over long distances with minimal loss. This ensures that the transmitted data remains strong and clear, reducing the need for additional amplifiers or signal boosters.
- Durability: Feeder cables are designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures, moisture, and UV radiation. This makes them suitable for outdoor installations where durability is critical.
- Shielding Against Interference: The double shielding of RF feeder cables ensures that external electromagnetic interference does not affect the transmitted signal. This is especially important in environments with high levels of interference, such as urban areas or industrial settings.
- Wide Frequency Range: RF feeder cables are designed to operate across a broad frequency range, making them versatile enough for a variety of applications, including telecommunications, broadcasting, and wireless communication.
- Cost-Effective: Feeder cables provide a cost-effective solution for transmitting high-frequency signals over long distances. Their ability to maintain signal strength reduces the need for additional infrastructure, such as signal boosters or repeaters.
Choosing the Right Feeder Cable
Selecting the right feeder cable depends on several factors, including the application, frequency range, and environmental conditions. Here are some key considerations when choosing a feeder cable:
- Cable Impedance: The impedance of the cable is one of the most critical factors to consider. For most RF applications, a 50 Ohm RF feeder cable is the preferred choice, as it provides the best balance of low attenuation and durability.
- Frequency Range: Consider the frequency range of the signal that will be transmitted through the cable. Low-frequency signals may require a different type of feeder cable than high-frequency signals.
- Environmental Conditions: If the cable will be installed outdoors, ensure that the outer jacket is UV-resistant and waterproof. For indoor applications, cables with flexible and durable jackets are ideal.
- Cable Length: The length of the cable can impact signal loss. Longer cables will experience more attenuation, so it’s essential to choose a low-loss feeder cable for long-distance transmission.
- Manufacturer Quality: Choosing a reputable RF feeder cable manufacturer is critical to ensure that the cable meets industry standards for performance and durability. Look for manufacturers that offer quality assurance and adhere to international standards.
Conclusion
Feeder cables, especially RF feeder cables, are essential components in communication systems that require reliable, high-frequency signal transmission. Their low signal loss, durability, and versatility make them suitable for a wide range of applications, including telecommunications, broadcasting, military, and wireless communication. When selecting a feeder cable, consider factors such as cable impedance, frequency range, environmental conditions, and manufacturer quality to ensure optimal performance for your specific needs.
Investing in a high-quality RF feeder cable ensures that your communication system operates efficiently, with minimal signal degradation and interference.